Google penalties are a form of action against content spam. Like manual actions, penalties are sent by Google to penalize websites that violate search engine policies. Unlike manual actions, penalties are typically issued only after content spam has been identified. But penalties can still have an impact on rankings, so they’re worth monitoring.
Penalties can have both direct and indirect effects on search engine rankings. They’re designed to educate websites about content spam-related guidelines and encourage action to resolve the violation, but they can also severely hurt a site’s search engine rankings.
This blog will cover penalties like manual action types (AMPs), reconsideration requests, and user-generated spam.
What is a Google penalty?
A Google penalty is a punishment given to websites for violating the search engine’s guidelines and policies. The penalties vary depending on the type of violation and can be either automated or manual penalties.
- When a keyword-level penalty is given, it refers to penalties imposed on a particular keyword’s search results. The keyword may be demoted from the results or completely removed from appearing in search results.
- A URL-level penalty occurs when a link to a website is penalized for spamming that keyword with links that are unnatural, low-quality, or spammy. In this case, the link may be a demotion or removed from search results.
- A hostname-level penalty occurs when the webmaster uses too many keywords in the webmaster name or other meta tags of the website. This type of penalty can be given to webmasters if they use keywords excessively in the webmaster tag of their content or in the meta tags of their website.
- A domain-wide penalty occurs when webmasters use spammy keyword stuffing tactics such as keyword stuffing on multiple domains or using unnatural keywords over and over again. In this case, webmasters can lose the rankings of all their websites.
- A manual action by a Google employee is used to take down entire domains from search results due to low-quality content or violations of TOS & policies.
A few types of penalties include keyword level, URL level, hostname level, domain level and delisting penalties. Each type varies in severity based on the type of violation and how many times it has happened before.
Penalties are an important part of ensuring quality content is served on search engine results pages (SERPs).
On-page guideline violations and related notifications
– On-page guideline violations are problems identified on a website that can lead to a manual action from Google.
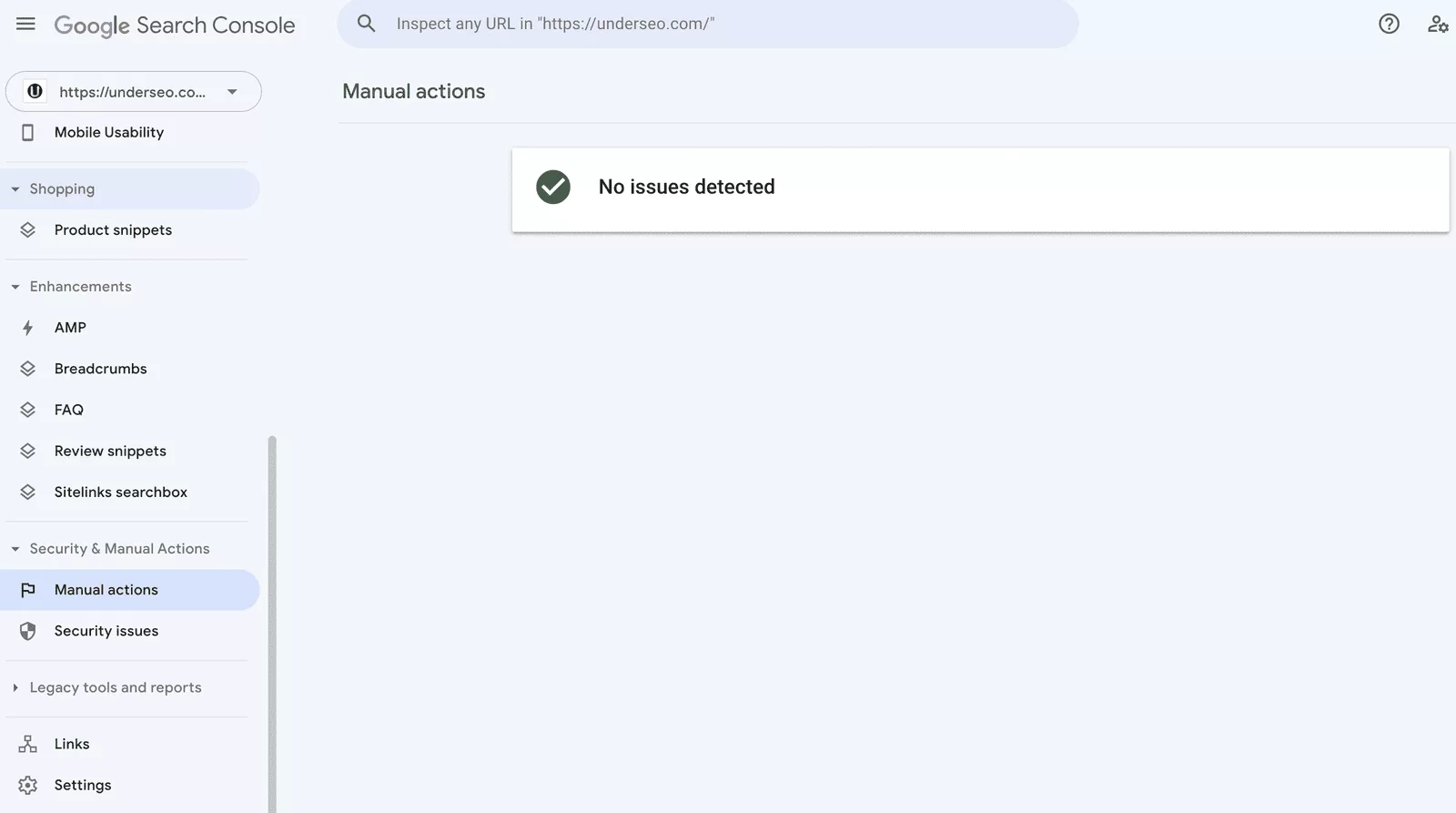
– A manual action is a temporary action taken by the search engine ranking team against a webmaster’s entire website or a single page to address violations of webmaster guidelines.
– Manual actions can be issued against a single page or an entire website, requiring immediate attention.
– A notification from the search console means that a manual action has been taken against your web property and will tell you the exact problems they found and on which pages they appear to help you fix the issue.
– If you have received a notification, it is important to review the action and make necessary corrections. If you haven’t received a notification yet, check with your webmaster advocate for assistance and follow the steps specified in the manual actions notification email.
Request Free Review
We start by reviewing your website and then take a look at your current ranking in SERPs.
- Unlock Your Website’s Potential with Our Comprehensive Analysis.
- Outrank Your Competitors with Our Expert Insights and Recommendations.
- Ways for increasing website traffic.
- Get Tailored Recommendations to Achieve Better Results Online.
Major and pure spam problems
Google takes manual action against websites that engage in spammy content and behavior. Pure spam is one of the most severe manual actions and usually results in the entire website being removed from organic search. A manual action notification will be sent to site owners if Google identifies the page content as entirely spammy.
Other penalties that may be applied to an individual page or an entire website include thin content, low-quality content, or low-quality links. A third-party spam penalty is usually applied to a part of a domain and Google tries to scope it precisely. This helps ensure that only the spammy content on a particular web page or website is affected rather than the entire domain.
Spam problems
Manual penalties can be applied for a variety of thin content and spammy content violations. These penalties include warnings, low-quality manual rating, and removal from search results.
If a reconsideration request is rejected, it is likely due to persistent violations such as unnatural inbound links or spammy content. Causes of manual penalties may include unnatural links, thin content, hacked website, pure spam, cloaking or sneaky redirects, hidden text, keyword stuffing, or spammy structured markups.
If a website does not adhere to the on-page guidelines, it could receive a ‘NotFound’ or ‘404’ error message when users search for it on Google Search. This would mean that the website has been removed from the search results and manual action has been taken against it. However, manual actions are not the only way that Google can take action against thin content and spammy content on websites. It also uses machine learning algorithms to identify potentially spammy pages and take action against them automatically.
Thin content
In general, thin content includes pages with little value, such as doorway pages, auto-generated content, low-quality content, and scraped content. Such pages can result in penalties from Google. Low-quality or duplicate content can also lead to penalties.
Google does not favor websites with heavily monetized affiliate content or scraped content. Instead, it prefers websites that include high-quality original content. To avoid penalties, websites should optimise content with low-quality or duplicate content and include high- quality content.
Besides, Google recommends avoiding thin value pages with little useful details and insufficient unique content. Instead of stuffing your web page full of links and information without a clear purpose, focus on providing valuable and unique content to distinguish yourself from the competition.
News and Discover
Page guideline violations can lead to penalties from Google. While there is no cap on the total number of reconsideration request attempts, it’s important for webmasters to manually remove as many toxic links as possible and submit the remaining links to Google in the form of a disavow file.
This will help ensure that search results are not impacted by the link violations. If the efforts to get back into Google’s good graces are deemed insufficient, a reconsideration request rejected message is issued. It’s critical that webmasters follow these steps to avoid penalties and maintain a healthy search engine optimization (SEO) profile.
When submitting a reconsideration request, a disavow file should be uploaded first and confirmation of the change should be received. Additionally, webmasters should continue to work towards improving their search engine rankings by focusing on high-quality links and content on their website.
There is no cap on the total number of reconsideration request attempts, so it’s important for webmasters to continuously improve their search engine optimization efforts and stay ahead of any algorithm updates from Google.
AMP content mismatch
AMP content needs to match the canonical version of the same page, which may not always require content to be word-for-word. For example, when a web page contains an advertisement, AMP content should display the advertisement without any additional copy or banner. To ensure content is consistent between AMP and canonical pages, Google’s penalty for AMP content mismatch includes penalties for specific violations.
For instance, if content on one page is not canonical with AMP content on another page, the penalty may include a manual action or notification from Google. When users request reconsideration of penalties due to AMP content mismatch, Google takes into consideration various factors and may reconsider the action or notification if it is in user’s best interest.
Cloaking and redirects
Google considers cloaking and redirects to be against their guidelines and can result in manual action being taken against a site. A search engine prefers to rank the final destination page instead of an intermediary landing page. For example, if a user types in “Google” and clicks on the search results, Google would prefer to show the results directly from the search engine rather than from a redirect page.
When searching for information on the web, users typically click links that lead them to different pages with relevant content. However, webmasters may use cloaking and deceptive redirects to send users from one URL to another without indicating this change of location. This practice can lead to search engines ranking pages that are not the original destination page instead of the main content on a website.
– Cloaking is considered to be deliberate attempts by webmasters to manipulate search results and can result in penalties, such as low rankings or manual action being taken against a site.
User-generated spam
User-generated spam on Google can result in a penalty. This penalty is usually applied to websites where users create the spam, such as forums. Common types of user-generated spam include links to malicious content or links to payday loans or other harmful websites. Comment spam, which is also against Google guidelines, can be caused by automated programs creating links, which is against Google’s guidelines. If user-generated spam is found on your website, it could result in pages being removed from the index and make it harder for users to find relevant content. To avoid manual action notification from Google, moderation of comments is essential.
Hacked content spam
Hacked content spam is when a website is compromised and malicious or irrelevant content is injected without the site owner’s consent. Hacked content spam penalties are applied to sites that are user-driven and where the vulnerability isn’t caused by poor quality enforcement, but rather insufficient security. If a site is affected by hacked content spam, it can result in a prominent label in SERPs, warning users of the possible threat if they open the website. To avoid hacked content spam, it is important to ensure that website security is up to date and to be aware of any suspicious activity on the website.
Incorrect structured data
It’s essential to respect Google’s guidelines regarding structured data. Violating these guidelines can lead to manual penalties and potentially serious consequences for a search engine optimization (SEO) or web page optimization (WPO) campaign.
Possible manual penalties include a lowered page ranking in the search results or an action taken against your web page. Such actions can include removing content, suspending or deleting pages, or taking other actions that may significantly harm your site’s visibility in search results.
Additionally, incorrect structured data highlighting may result in the removal of rich snippets from search results. If you have violated this guideline, you must review all proper markups to identify any that violate Google’s guidelines and remove or update them, then request a reconsideration.
Unnatural outbound links
Unnatural links have been a cause of concern for search engine optimization (SEO) experts for years. These unnatural links can come from different sources, such as web spam, keyword stuffing, anchor-heavy links, or cloaking. When unnatural links are detected by search engines, they may be penalized and removed from search results.
In some cases, the unnatural links may be permabanned permanently. If unnatural backlinks continue to be detected after manual action has been taken on an individual website, search engines may also issue a manual action notification to that site’s owner.
When dealing with unnatural backlink penalties, it’s important to explain the details of your reconsideration request. This will allow search engine optimization experts to show why the unnatural link should be reinstated in search results. Unnatural backlinks can be damaging not only to a website’s visibility but also its credibility in the search results.
Spammy free host
Google may issue manual penalties when a free web hosting service is heavily burdened with spammy pages. It tries to scope spam precisely to avoid imposing manual action on the whole domain. When spam is detected on multiple websites hosted by the same web host, Google usually penalizes all the websites. Aggressive spam methods may lead to a “Pure Spam” penalty.
This type of penalty results in the removal of the website from Google’s index, which can have a dramatic impact on user experience and rankings. keyword stuffing and other aggressive spam types can result in a “Pure Spam” penalty.
Manual Action Types (Google Penalties)
– penalties – manual action types are penalties applied to websites by Google after manual review. A manual action can vary from keyword-level penalties to site-wide penalties.
– keyword-level penalties are penalties added to a website’s search rankings as a result of content that is violation of the search engine’s guidelines.
– site-wide penalties are issued when a website is in violation of any of the search engine’s guidelines, irrespective of the keywords or pages on which the violation is made.
– algorithmically-issued penalties are penalties issued by the search engine algorithm without manual intervention, such as demotion or suspension of a web page from the search results.
– manual action can be issued by a Google employee, who would first review a web page and then take action on it.
– manual action can take various forms, such as issuing de-indexing penalties for content that violates guidelines, issuing manual spam flags for spammy content, etc.
– there are various types of manual actions and each has its own set of criteria and process
Penalties can either be algorithmically or manually issued depending on the type of action taken. A manual action can take various forms like issuing de-indexing penalties for content that violates guidelines, issuing manual spam flags for spammy content, or taking other actions such as disabling a web property’s access to webmaster tools. In all these cases, there are several factors that would play an important role in terms of how and why action might be taken by a manual action team member.
Keyword stuffing
Manual Actions (Google Penalties) can be caused by keyword stuffing, which is an attempt to manipulate search engine results. Keyword stuffing is a common cause of manual action penalties as it can overload search results with irrelevant keywords or cause duplicate content. Other common manual actions include removing links from search results and deindexing websites from Google search. When manual actions are issued from Google’s webspam team manually reviewing a website, they can vary in severity and may result in partial or entire removal of website content from search results or an entire website being de-indexed.
Comment Spam
Manual action penalties, also known as manual penalties, are issued after Google’s web spam team manually reviews a website. Comment spam can lead to a manual penalty being issued if there are unnatural links or keyword stuffing on the website. This can result in content from search results being removed or an entire website being deindexed. Manual penalties are applied by human reviewers who evaluate your site based on Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines. This means that manual action penalties may vary depending on the type of manual action detected and specific guidelines used to assess search quality.
When commenting on blog posts or reviewing news articles, it’s important to be respectful and engage with the content at hand. This helps improve user experience and the credibility of the content on your site.
User-Generated Spam
User-generated spam is when users create pages of spam content. This action can be punishable by manual actions, which are penalties issued by Google for violating the company’s quality guidelines and policies. Manual actions can range from thin content, to hacked websites, unnatural links, or other violations of the search engine’s guidelines.
When user-generated spam is detected, Google will typically issue a manual action of some type to penalize the offending pages or domain. These penalties can range from thin content penalties to unnatural links penalties or entire domain penalties. Depending on the type of manual action and the violation that was detected, the user-generated spam action can result in a manual action penalty of its own.
The manual action types such as user-generated spam are discussed in detail on Google’s webmaster blog to help users understand how manual actions work and why they may be issued to pages or domains with user-generated spam content.
What is user-generated spam?
User-generated spam is any content that attempts to manipulate search engine rankings or mislead users. Keyword stuffing and link schemes are common types of user-generated spam that can significantly impact Google rankings.
Manual action penalties by Google occur after their webspam team manually reviews a website for violations of their guidelines. If manual action penalties are issued, website owners will receive a notification through Webmaster Tools. This notification will allow website owners to identify the type of manual action penalty they have received and take action to improve their content. Website owners can use Webmaster Tools to identify the type of manual action penalty received and take appropriate action, such as editing the content or removing it from search results.
Manual action penalties can result in demotion or even banning a website from Google search results, depending on how severe the violation is. However, manual action penalties are only issued after a thorough review by Google’s web spam staff and do not always lead to these drastic results.
Automatically Generated Content
Automatically generated content is content that is generated through certain programs or systems without adding any value to the user experience. Such content can be problematic for users looking for high-quality content and may lead to user confusion or dissatisfaction.
Manual action can be taken if websites are using AI to create content instead of employing writers. If a website is in violation of Google’s guidelines, manual action may be necessary. This action can include penalties like site-wide penalties, manual action, or manual review of individual webpages.
If auto-generated content is rich in keywords or their synonyms but makes no sense to the reader, it can be a problem for search engine optimization (SEO) and user engagement. To ensure that users receive quality content, manual action should always be taken when automatic content creation results in poor user experience.
Sneaky Redirects
Sneaky redirects are when users are redirected to content different than what they searched for. This can result in user experience issues and violate Google’s webmaster guidelines. Poorly implemented scripts and hacking attacks can also be responsible for sneaky redirects.
Manual action may be imposed by Google as a penalty if redirects are used for manipulative purposes. Redirects can be used for legitimate purposes, such as moving a website to another domain or consolidating several pages into one. A manual action action can be avoided if the website is adapted to mobile device requirements or if redirects are used to an internal page when users log into the portal.
Affiliate Programs
Google penalties are a type of manual action that Google takes against websites that violate its policies. These penalties can range from warnings to more serious manual actions, such as removing content, suspending services, or taking other action against the website. In some cases, penalties may temporarily disable access to content on a website.
Affiliate programs are an important part of the Google marketing ecosystem and can be penalized if affiliate sites violate Google’s policies. This is why notification mechanisms like notification banners and email alerts are put in place to ensure website owners are aware of potential issues with their site. Such notification can help website owners to quickly resolve any issues and avoid penalties.
When a website owner receives notification of potential violations of Google’s policies, manual actions can be taken by Google to penalize the site, such as temporarily disabling access to content or redirecting users to another page.
Scraped Content
Google manual penalties can be applied to websites that are deemed in violation of the Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines. These penalties typically range from partial to site-wide penalties, and can be implemented by human reviewers at Google. Algorithmic penalties, on the other hand, are a result of changes to Google’s algorithm which can cause organic rankings and traffic to drop. Manual and algorithmic penalties are two types of Google penalties that can result in dramatic drops in rankings and organic traffic.
When manual penalties are triggered by content scraped from other websites, it is commonly due to content that violates Google’s guidelines or policies. This content may include spammy links,invalid duplicate content, or intrusive advertisements. Some webmasters have also been penalized for scraping content from other websites without permission or legal citation. Scraped content, therefore, can trigger manual penalties from Google if it is against their guidelines.
Doorway Pages
Google can take various actions against your website, including penalizing it with a Google penalty or sending a manual action notification. These actions can range from issuing warnings and taking down the website to simply not showing results for specific keyword rankings.
Doorway pages are pages that are linked from other Google domains but do not have their own website. These pages can be penalized for duplicate content and low-quality links. Manual actions can include anything from removing links to issuing warnings and taking down your website. It is important to understand the types of actions that Google is capable of taking and take appropriate steps to rectify any issues.
Cloaking / Hidden Texts and Links
Manual action can be taken against sites that engage in cloaking or sneaky redirects, hidden text or keyword stuffing. Cloaking is a sophisticated black hat technique that attempts to show search engines a different version of the website than the one visitors see. Hidden text and links can also cause manual action. These pages may contain keywords, keywords in disguise, keywords with hidden content, or keyword-stuffed headlines. Flash pages, invisible text, redirects to spam domains, and other sneaky redirects can also lead to penalties for a website.
Backlink Violations
Google’s web spam team may issue manual action when a website violates its webmaster quality guidelines. These manual actions can affect a single page or an entire website, resulting in a demotion in search results or removal from search results altogether. Manual actions must be addressed immediately to restore rankings and visibility in search results.
If a manual action is issued for an unnatural backlink scheme, keyword stuffing, or excessive link exchange, it must be immediately removed and actioned to prevent further penalties. Otherwise, the user’s website may experience severe penalties such as loss of rankings and visibility in search results. To avoid manual action penalties, users must ensure that their websites are compliant with webmaster quality guidelines and avoid violating Google’s rules.
Structured Data Spam
Structured data spam can result in manual action from Google, causing certain rich search results to be removed from SERP. This action can be partial, only applied to a certain page, or site-wide, which can dramatically impact user experience. To avoid manual action from Google, content must be correctly marked up and follow the guidelines provided by the search engine. Automated content, including keyword stuffing and meaningless content, can also be subject to manual action. It is crucial for webmasters to follow all of the guidelines provided by Google in order to ensure high-quality search results and avoid penalties. If you are facing penalties for keyword stuffing or other unnatural content on your website, it is important to understand why and how you were detected so that you can improve your search engine optimization strategy moving forward.
Content with Little Value / Thin Value
In cases of low quality content, manual action may be issued against pages containing automatically generated texts, poor-quality guest posts, or republished content. For example, manual action may be taken against pages that contain articles written by someone other than the original author or blog posts that have been copied and pasted from other websites.
Such content is low-quality and adds little value to a user. Additionally, hiring a content creator to create bad articles can lead to penalties on your website. Low-quality content is defined as content which adds little or no value to a user. Quality content is an essential part of a successful website. These actions are meant to ensure that users are presented with valuable and engaging content on your blog or website.
Pure Spam
Google penalties, or manual actions, are issued by the web spam team after manually reviewing a website for potential spam. Such actions can result in partial removal of website content or complete deindexing of the website from search results.
A manual action may result from keyword stuffing, unnatural links, duplicate content, unnatural keyword use, and other spam-like practices. In some cases, a manual action may lead to further action, such as account suspension or removal. Manual penalties are typically applied by human reviewers at Google who assess a site based on Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines. If a manual action is issued against a website, the owner will receive notification in Google Search Console and be able to appeal the decision.
Request Free Review
We start by reviewing your website and then take a look at your current ranking in SERPs.
- Unlock Your Website’s Potential with Our Comprehensive Analysis.
- Outrank Your Competitors with Our Expert Insights and Recommendations.
- Ways for increasing website traffic.
- Get Tailored Recommendations to Achieve Better Results Online.

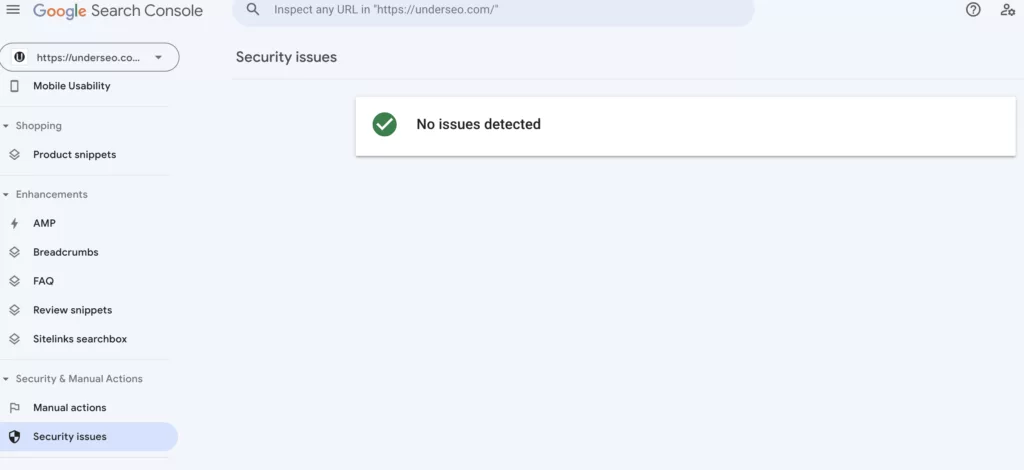
Security Issues
A manual action can be issued by Google’s web spam team after a website has been manually reviewed. A manual action can be either partial or complete removal of website content from search results. This action is taken when a search engine has found problems with the content of a website, and human review is required to determine whether the issues are justified.
To issue a manual action, search engine users must follow quality guidelines outlined in the Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines. If a manual action is applied to a website, a notification will be sent via Google Search Console. Google penalties can be issued if a website violates their Webmaster Quality Guidelines and poses an increased risk of harm to users or business.
This action is taken when search engine users feel there is poor quality content on web pages, such as duplicate or low-quality content, and they must manually remove that content to improve user experience.
Manual action types are an important tool for search engines to maintain quality of search results and user experience. They help search engines identify websites that need manual action and ensure that they comply with quality guidelines before results are returned to users.
Google News & Discover Manual Actions
Sites that violate Google News and Discover policies may receive manual actions from Google, which can be seen in the Search Console. Manual action warnings are typically issued regarding content mismatch between the canonical web page and the AMP version. Buying links or participating in link schemes to manipulate PageRank is a violation of Google Webmaster Guidelines, and can result in manual action. To prevent manual action, make sure to follow Google’s structured data guidelines and remove any spammy accounts from your site.
After making changes to comply with guidelines, request a review in Search Console to have the manual action revoked. If you still receive manual action warnings after making necessary changes, request a reconsideration request to ensure that the manual action is removed.
Reconsideration requests and related notifications
If you’re a webmaster and have had manual action taken by Google for a penalty, you may be eligible to request reconsideration. This is a formal review process to reconsider the action taken on your behalf. If a webmaster has made good-faith efforts to resolve the issue and the issues remain unresolved, a reconsideration request could be accepted.
Possible reasons for reconsideration include if manual action was incorrectly assessed or if there was some other error. However, repeated reconsideration requests are not guaranteed turnaround times. It’s imperative that webmasters follow the steps outlined in the notification email to request reconsideration as accurately and quickly as possible.
The notification email will include detailed instructions on how to submit a request and confirmations of receipt of the request. It’s important to note that if the manual action is upheld, the webmaster will need to appeal the action through Google’s webmaster forums.
Disavow file updated notification
When a user uploads an update to their disavow file, Google gives a notification. This is to ensure that users review and confirm the changes before submitting documentation to Google. In most reconsideration requests, Google processes them quickly and either approves or rejects them based on the quality of the request.
However, there are some edge cases where reconsideration requests can take longer than expected. If the efforts are deemed insufficient, a reconsideration request rejected message will be sent. Repeated reconsideration requests are allowed but with a limit on how many requests a user can make within a given period of time.
Frequently Asked Questions
What could lead to Google issuing a manual penalty?
Depending on the specific violation, Google may issue a manual penalty to a website. Some of the most common violations that can lead to a manual penalty are spammy content, violating webmaster quality guidelines, and low-quality links.
After evaluating the website against their guidelines, human reviewers at Google may issue a manual action penalty such as removing website content from search results, deindexing the entire website, or issuing a notification to the website owner. These penalties are generally done algorithmically and do not require human intervention.
What is a manual penalty from Google?
If you’re wondering what is a manual penalty from Google is, then it’s basically a process where a human reviewer looks at the content of your website and determines that it violates webmaster quality guidelines. This can take the form of partial or site-wide removal of content from search results or even the complete deindexing of a website.
Receiving a manual penalty means that this review has been conducted and the results are in. It’s important to keep in mind that manual penalties are issued after Google’s webspam team manually reviews a website.
So if you’re worried that your website might have received such a review, then you should contact Google directly to inquire about the status of your website.
What kind of Google penalties can you get?
When it comes to penalties from Google, manual penalties can be given by Google auditors, while algorithm-generated penalties may result from spammy or low-quality content on your website. Common causes of manual penalties include keyword stuffing, hidden links, duplicate content, and irrelevant keywords.
Algorithm-generated penalties may range from a single URL penalty to de-listing of an entire domain from Google search results. To avoid penalties, make sure to follow Google’s guidelines and policies when building and maintaining your website.
Google Search Console (formerly known as Google Webmaster Tools) is where you’ll be notified of website issues that may negatively impact visibility in Google search results. By using this web tool, you can diagnose any issues and take action to correct them before they cause any further damage.
What happens when you get a Google penalty?
When a website receives a Google penalty, it means that a person has reviewed the content and determined that it violates their Webmaster Quality Guidelines. This could be due to keyword stuffing, hidden links, duplicate content, irrelevant keywords, bad redirects, spyware, adware, and viruses. In some cases, this could even mean that data issues were present on the website as well.
Google penalties can be given automatically by Google’s algorithms or manually by a human auditor. The manual penalty process is typically used for more severe issues.
Conclusion
Google penalties and manual action types are no joke. If you don’t follow the manual action guidelines laid out by Google, you could get penalized and have to take action to get back on track. You can request reconsideration of penalties or manual action types through a manual action request email. Read more about manual action requests here.
It’s essential to understand Google penalties before taking any action. There is a lot of content that companies can learn from other websites – but it only works when it’s helpful content, not spammy content. So if you’re looking for some tips on how to create quality content, read this blog.